Gold jewelry production is a symphony of technical prowess and artistic finesse, intertwining traditional methods with cutting-edge technologies. This article delves deeper into the intricate processes involved, from mining the raw material to crafting the final masterpiece, highlighting the technical nuances that underpin each stage.
Exploring Gold Mining and Refining
Gold extraction begins with mining operations, where various techniques such as cyanidation, heap leaching, or flotation are employed to recover gold ores from the earth’s crust. Once extracted, the raw gold undergoes refining processes such as smelting, electrolysis, or aqua regia dissolution to achieve high levels of purity. Advanced analytical techniques, including spectroscopy and X-ray fluorescence, ensure precise control over the refining process, minimizing impurities and optimizing the gold’s quality.
Alloying and Metallurgy
Alloying gold with other metals is a critical step in jewelry production, enhancing its strength and altering its physical properties. Metallurgical principles govern the alloying process, where precise ratios of base metals such as silver, copper, or palladium are blended with gold to achieve desired characteristics. Advanced metallurgical analysis tools, such as scanning electron microscopes and atomic absorption spectrometers, aid in controlling alloy compositions with exceptional accuracy, ensuring consistency across production batches.
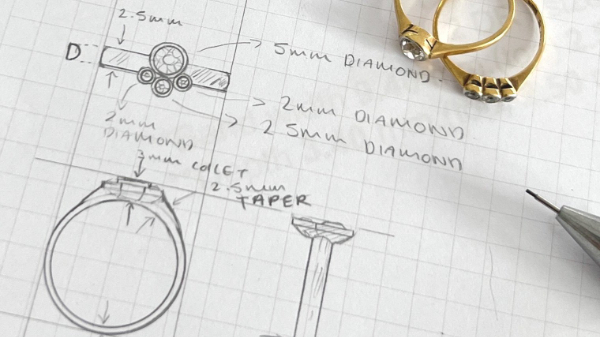
Design Engineering and CAD Modeling
Modern jewelry design blends traditional aesthetics with digital precision, employing computer-aided design (CAD) software to create intricate patterns and geometries. Design engineers leverage CAD modeling techniques to visualize concepts, simulate manufacturing processes, and optimize designs for efficiency and aesthetics. Finite element analysis (FEA) tools are used to assess structural integrity and material performance, enabling designers to refine designs for durability and wearability while minimizing material waste.
Additive Manufacturing and Rapid Prototyping
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, revolutionizes the prototyping and production of intricate jewelry designs. Utilizing technologies such as selective laser sintering (SLS) or stereolithography (SLA), jewelers can rapidly prototype complex geometries with high precision and resolution. This additive approach allows for iterative design refinement, accelerating product development cycles and minimizing time-to-market for new collections.
Precision Casting and Molding
Traditional casting techniques remain integral to gold jewelry production, where precision casting methods ensure the replication of intricate designs with minimal defects. Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is a prevalent technique employed by jewelers to create detailed wax patterns, which are then encased in ceramic molds and filled with molten gold alloys. Advanced casting equipment, including vacuum induction furnaces and centrifugal casting machines, enable precise control over casting parameters, ensuring consistent quality and dimensional accuracy across production runs.
Finishing and Surface Treatment
The final stage of production involves meticulous finishing and surface treatment to enhance the aesthetic appeal and durability of the jewelry pieces. Automated polishing and buffing machines impart a mirror-like finish to metal surfaces, while electroplating processes such as rhodium plating or gold plating offer additional protection against tarnishing and wear. Laser welding technology enables seamless repairs and adjustments, ensuring that each piece meets the highest standards of craftsmanship and quality.
Gold jewelry production represents a harmonious blend of technical ingenuity and artistic expression, where traditional craftsmanship converges with modern innovation to create timeless works of art. By embracing advanced technologies and metallurgical techniques, jewelers continue to push the boundaries of design and manufacturing, elevating gold jewelry to new heights of excellence and sophistication. As a testament to human creativity and mastery, each piece of gold jewelry embodies the essence of craftsmanship, destined to be cherished and admired for generations to come.